3.4. Data Source¶
A data source is a node in the workflow graph.
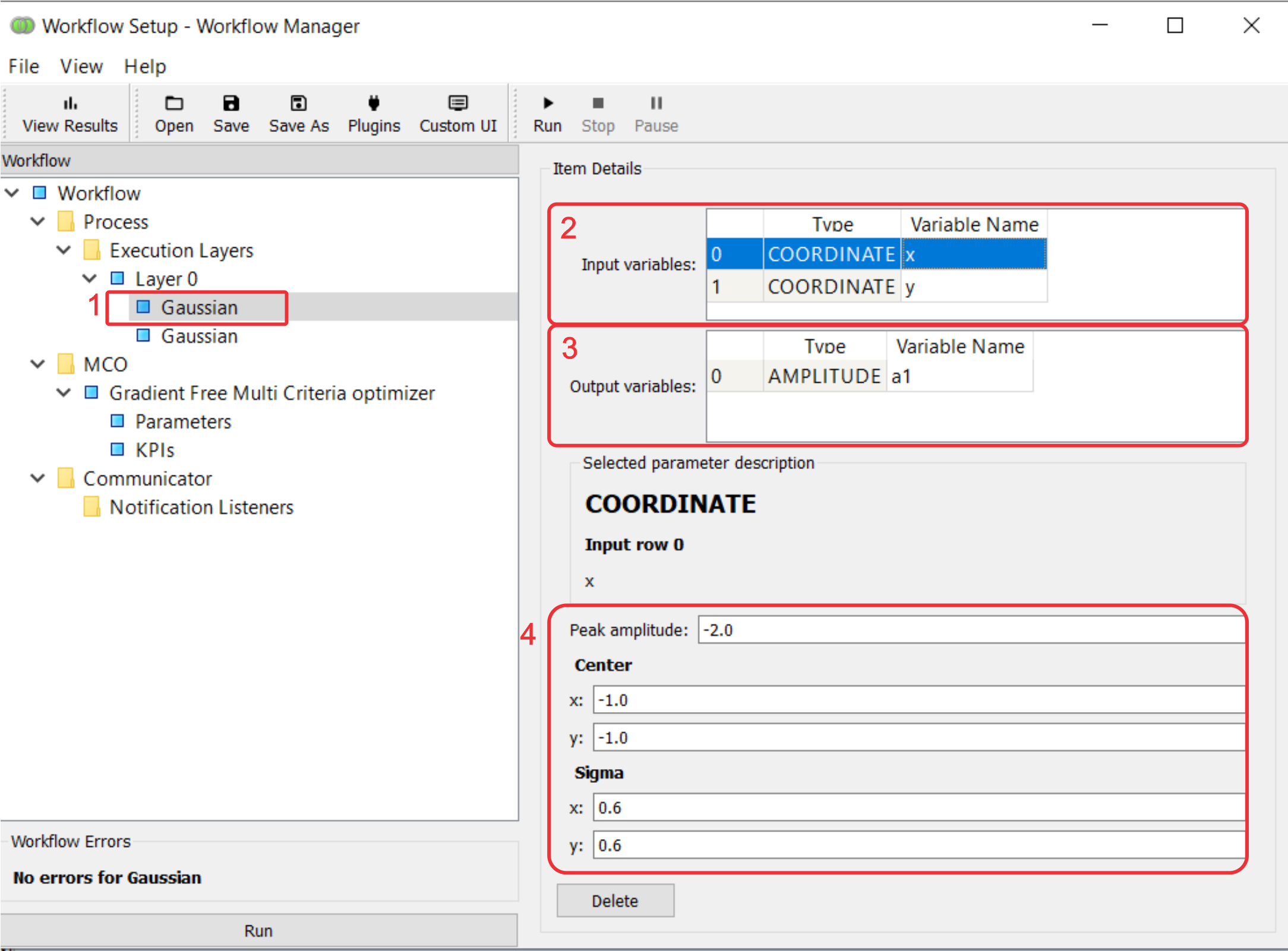
In the Workflow Manager, when you click on a data source, you will see its:
- function.
- The function that the node computes.
- inputs.
- The function’s parameters that can either be optimized (by selecting it as an
MCO Parameter) or fed from the outputs of other nodes (by setting its
variable nameto that of an output of another node).
- outputs
- The function’s returns that can be optimization criteria (by selecting it as an MCO KPI)
and/or be passed to the inputs of other nodes (by setting its
variable nameto that of an input of another node).
- internal parameters (model)
- The function’s parameters that are ‘internal’ to the node (are not node inputs). They cannot be optimized but can be set by the user in the Workflow Manager. Think of them as the function’s ‘constants’.
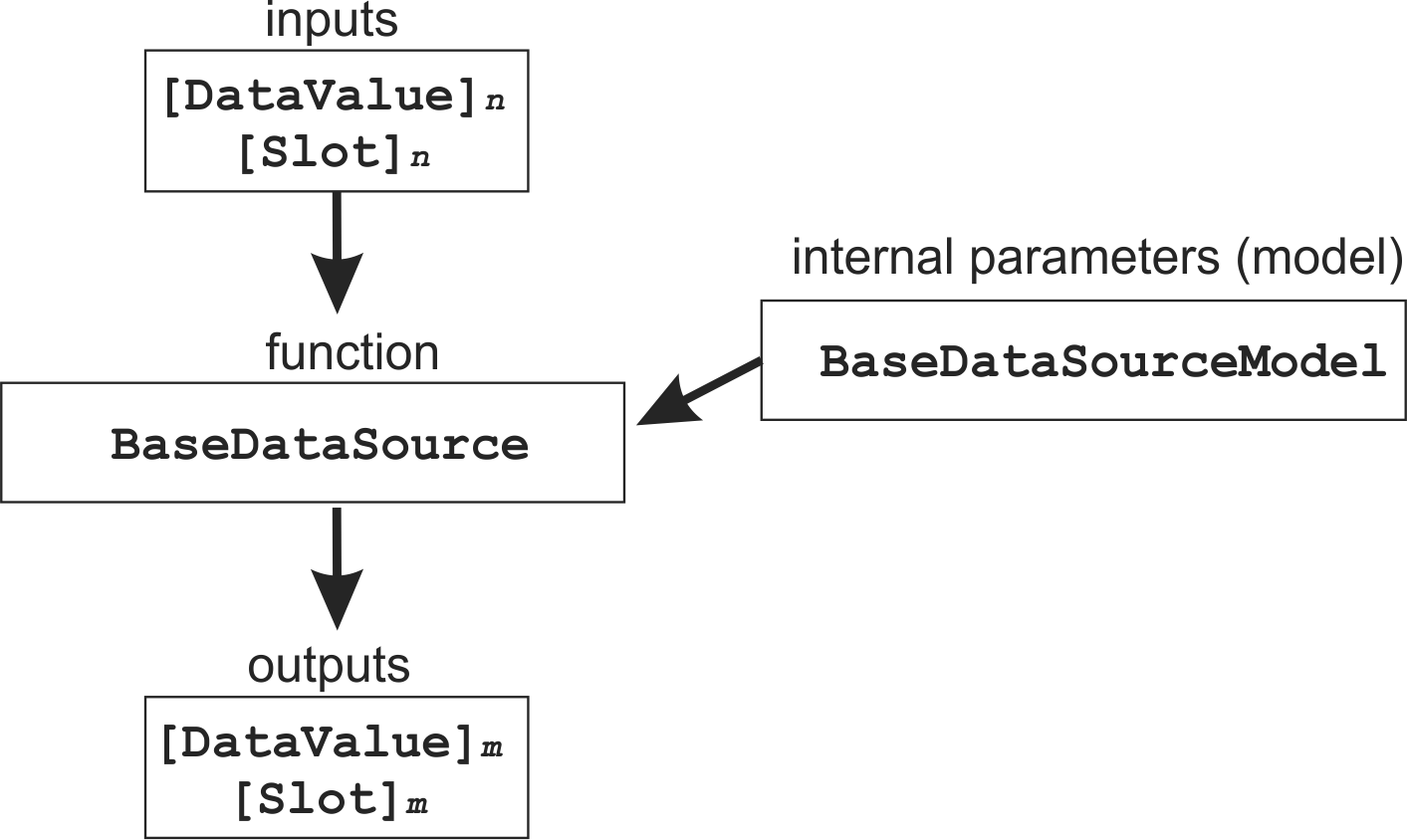
These aspects of the node are represented by a set of class objects:
We will illustrate how to design and use these objects, using the example of the Gaussian data source, a two-dimensional Gaussian on the xy-plane:
The source code for this data source can be examined here.
3.4.1. DataValue and Slot¶
Both these classes represent node (data source) inputs and outputs.
DataValue objects carry the actual value of an input/ouput and are passed between
connected node’s during execution of the graph/workflow. Their attributes are:
value. The value of the input/output.
type. The type of the input/output: a string that is meant to be a CUBA key.
name. The name of the input/output.
Slotobjects describe the input.output and are the UI (Workflow Manager) interface- to the DataValues. Their attributes are:
description. A description of the input/output.
type. The ‘CUBA’ key of the input/output.
These functions could be merged into a single class.
3.4.2. BaseDataSource¶
The node’s function.
class Gaussian(BaseDataSource):
def run(self, model, parameters):
x = parameters[0].value
y = parameters[1].value
a = ((x - model.cent_x) ** 2)/(2.0 * model.sigm_x ** 2)
a += ((y - model.cent_y) ** 2) / (2.0 * model.sigm_y ** 2)
a = model.peak * math.exp(-a)
return [
DataValue(value=a, type="AMPLITUDE"),
]
def slots(self, model):
return (
(
Slot(description="x", type="COORDINATE"),
Slot(description="y", type="COORDINATE"),
),
(
Slot(description="a", type="AMPLITUDE"),
)
)
The run method is the function itself. Its arguments are:
model- The
BaseDataSourceModelobject that contains the function’s ‘internal’ parameters or ‘model’parameters- The list of
DataValueobjects with the values of the node’s inputs, one element per input.
run() returns the list of DataValue objects that are the node’s outputs.
The slots method returns Slot objects corresponding to the node’s inputs and outputs, in the
form of a tuple
((<tuple of input slots>), (<tuple of output slots>))
The elements of (<tuple of input slots>) correspond to the elements of the parameters
argument of run. The elements of (<tuple of output slots>) correspond to the elements
of run’s return.
3.4.3. BaseDataSourceModel¶
The node’s ‘internal’ parameters
class GaussianModel(BaseDataSourceModel):
peak = Float(-2.0, label="Peak amplitude", desc="Amplitude of the peak.")
cent_x = Float(-1.0, label="x", desc="x coordinate of the peak.")
cent_y = Float(-1.0, label="y", desc="y coordinate of the peak.")
sigm_x = Float(0.6, label="x", desc="Width (standard deviation) along the x-axis.")
sigm_y = Float(0.6, label="y", desc="Width (standard deviation) along the y-axis.")
traits_view = View(
Item("peak"),
Group(Item("cent_x"), Item("cent_y"), label="Center"),
Group(Item("sigm_x"), Item("sigm_y"), label="Sigma")
)
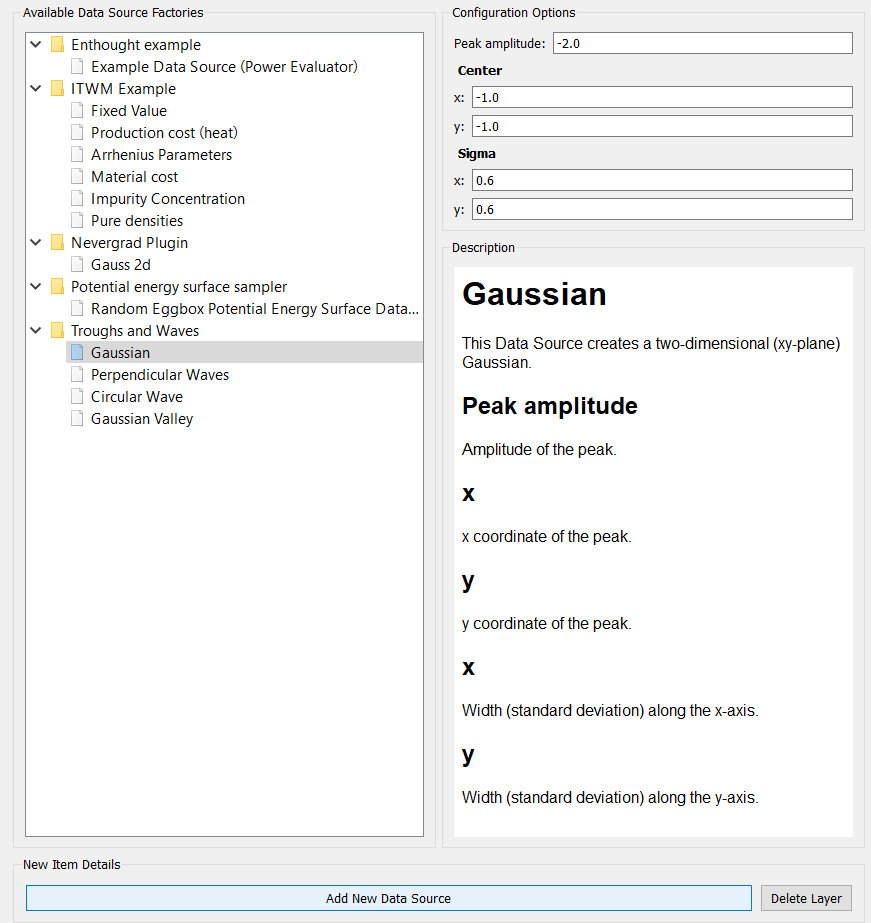
The label and desc attributes appear in the description of the data source
when it is selected from a plugin.
The View object determines how they are presented for editing in the Workflow Manager
(see above).
3.4.4. BaseDataSourceFactory¶
This is contributed to BDSS by the plugin and thus allows it to create instances of
BaseDataSource and BaseDataSourceModel.
class GaussianFactory(BaseDataSourceFactory):
def get_identifier(self):
return "gaussian"
def get_name(self):
return "Gaussian"
def get_description(self):
return "This Data Source creates a two-dimensional " \
"(xy-plane) Gaussian."
def get_model_class(self):
return GaussianModel
def get_data_source_class(self):
return Gaussian
The returns of the get_name and get_description methods appear in the description
of the data source when it is selected from a plugin (see above).